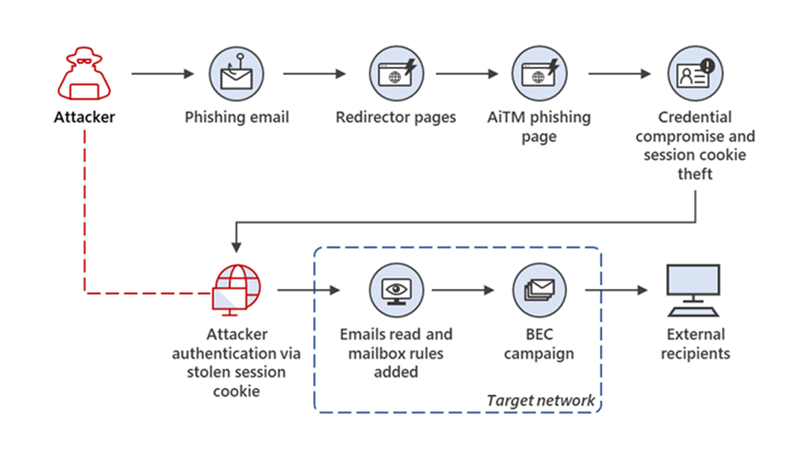
On July 12th, Microsoft announced that a large-scale phishing campaign used adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) phishing websites to steal users’ residential and perform business email compromise (BEC) campaigns against other victims. According to threat data, this phishing attack has targeted over 10,000 organisations who use Office 365 since September 2021.
Phishing is the first choice for many attackers who want to gain access to organisations and reports of this technique have rapidly grown over recent years. Microsoft’s 2021 Digital Defence Report revealed that phishing attack reports had doubled in 2020 and has become the most common type of malicious email.
Microsoft went on to describe the AiTM phishing process, disclosing that an attacker will attempt to “obtain a target user’s session cookie so they can skip the whole authentication process and act on the latter’s behalf”. This means that an attacker will not need to create their own phishing website and they can even automate the entire AiTM phishing process through open-source phishing toolkits.
The rise of this phishing campaign demonstrates how cyber threats will continue to evolve as users and organisations place forward various security measures to defend themselves. The technology used in such attacks is becoming more sophisticated and much larger in scale, so it’s important for users to remain cautious and implement best practices to protect their organisations.
Microsoft confirms that “While AiTM phishing attempts to circumvent MFA, it’s important to underscore that MFA implementation remains an essential pillar in identity security. MFA is still very effective at stopping a wide variety of threats; its effectiveness is why AiTM phishing emerged in the first place.”
Check out one of our articles to find out how to further prevent phishing!
Discover more tech news here!